From Industry 1.0 to 4.0 – How Far Has Manufacturing Come?

The manufacturing industry has evolved over centuries, from handcrafted goods to the state-of-the-art technology of today.
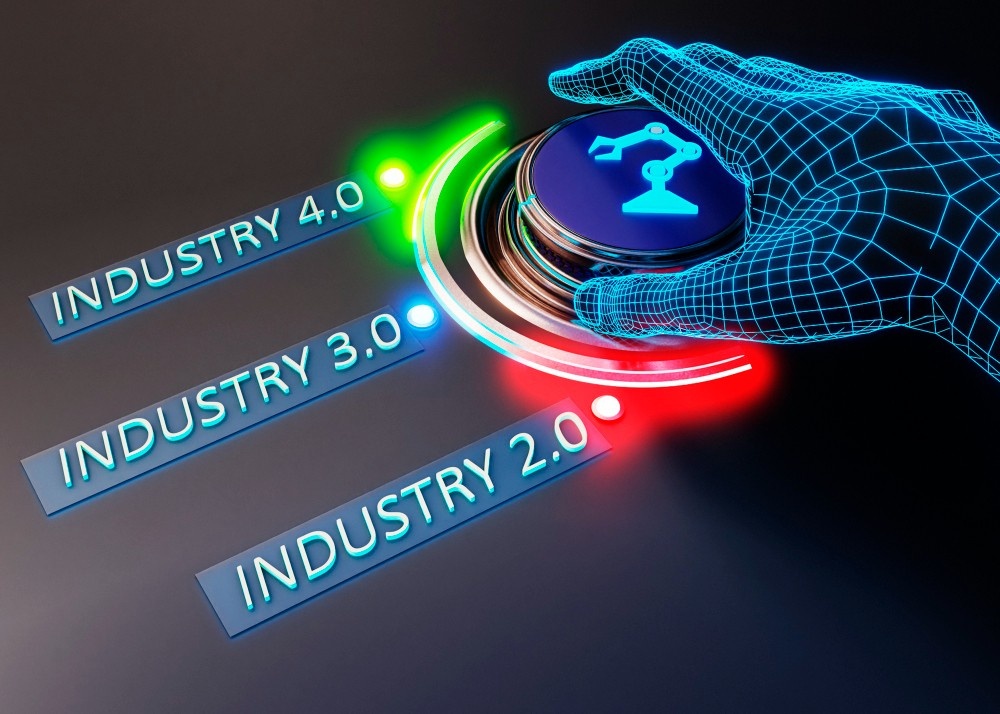
It’s been a long journey from Industry 1.0, which initiated the industrial age, to Industry 4.0, which is reshaping global production processes.
In this article, we will explore the journey of manufacturing, examining the milestones from Industry 1.0 to 4.0 and how these advancements have changed the landscape of modern manufacturing.
Industry 1.0: How Did It Begin?
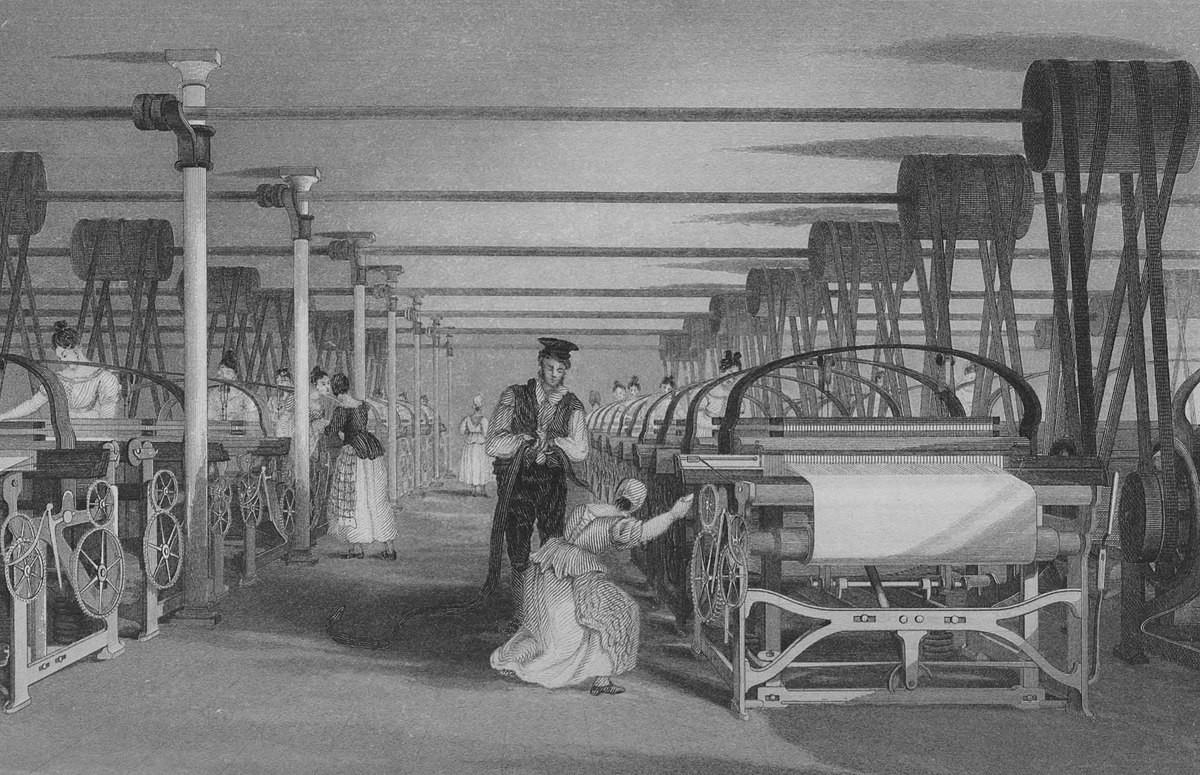

Illustrator T. Allom, Engraver J. Tingle
The first major shift in manufacturing occurred during the First Industrial Revolution, also known as Industry 1.0, in the late 18th century. It was characterized by the mechanization of production processes, largely driven by the introduction of steam engines and water power.
Before this period, goods were produced by hand in small workshops or by artisans, a labor-intensive process.
Industry 1.0 saw the invention of the spinning jenny, the power loom, and other machines that enabled factories to mass-produce textiles and other goods. This shift not only made production faster but also increased efficiency, marking the beginning of industrialization in Europe and North America.
The key focus during this period was to replace human labor with machines that could perform repetitive tasks at a faster pace. This led to the growth of factory systems as well as the shift from rural agricultural economies to urban industrial ones.
Industry 2.0: How Did It Change Manufacturing?
The Second Industrial Revolution, or Industry 2.0, took place in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. This era was marked by the introduction of electricity, which fundamentally transformed how factories operated. In this phase, industries expanded beyond textiles and into new sectors like steel, chemicals, and automobiles.
The development of the assembly line by Henry Ford in the early 20th century was a game-changer. It allowed for the mass production of goods at an unprecedented speed and efficiency.

Ford’s introduction of the moving assembly line in 1913 for automobile production reduced the time it took to produce a car from over 12 hours to just 90 minutes. This innovation not only lowered production costs but also made consumer goods more affordable.
In addition, Industry 2.0 saw the development of electric motors and better machines for precision, which allowed for the production of higher-quality goods in shorter time frames.
What Changes Came with Industry 3.0?
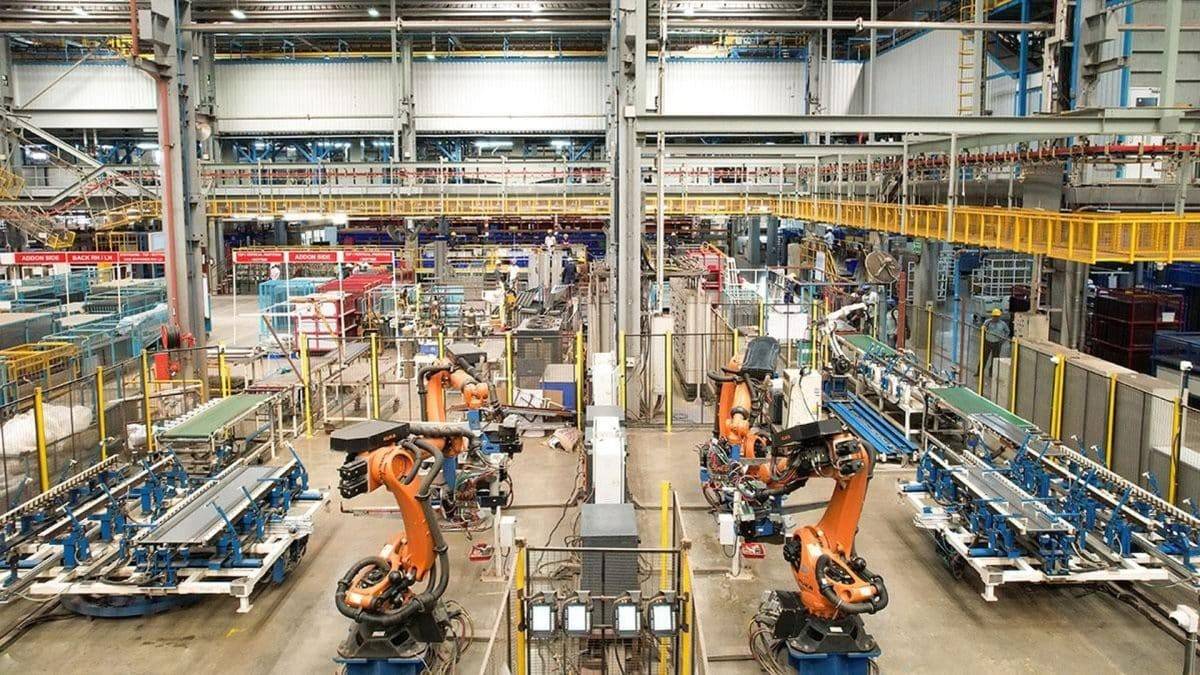

The Third Industrial Revolution, or Industry 3.0, began in the late 20th century with the advent of electronics, computers, and information technology. This era introduced automation to manufacturing processes, marking a shift from mechanical production systems to digital technologies.
In Industry 3.0, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and robots became integral to manufacturing plants. These machines could perform tasks like assembly, welding, and material handling with minimal human intervention. The widespread use of computers and software systems also helped streamline manufacturing processes, improving accuracy, speed, and productivity.
The rise of the internet allowed for the development of computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) systems, which connected various stages of production and facilitated data exchange between machines, operators, and managers. This era also saw the rise of just-in-time (JIT) production and lean manufacturing practices, which further optimized the use of resources and reduced waste.
Industry 3.0 focused on increasing automation and reducing human involvement in production processes, which significantly improved factory productivity and allowed for global supply chains.
Industrial 4.0: What’s New in Manufacturing?
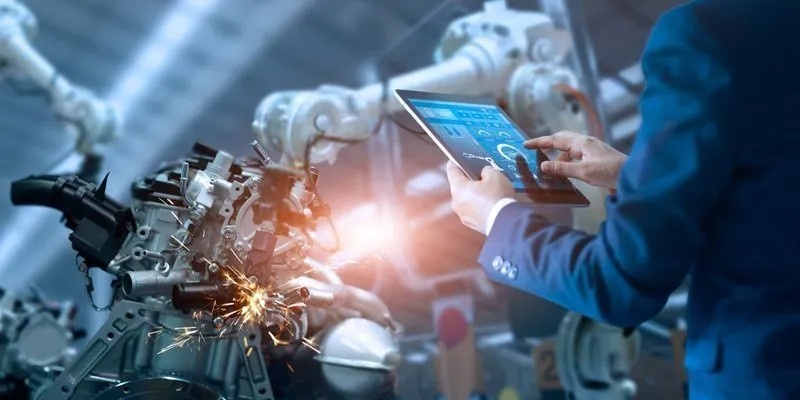

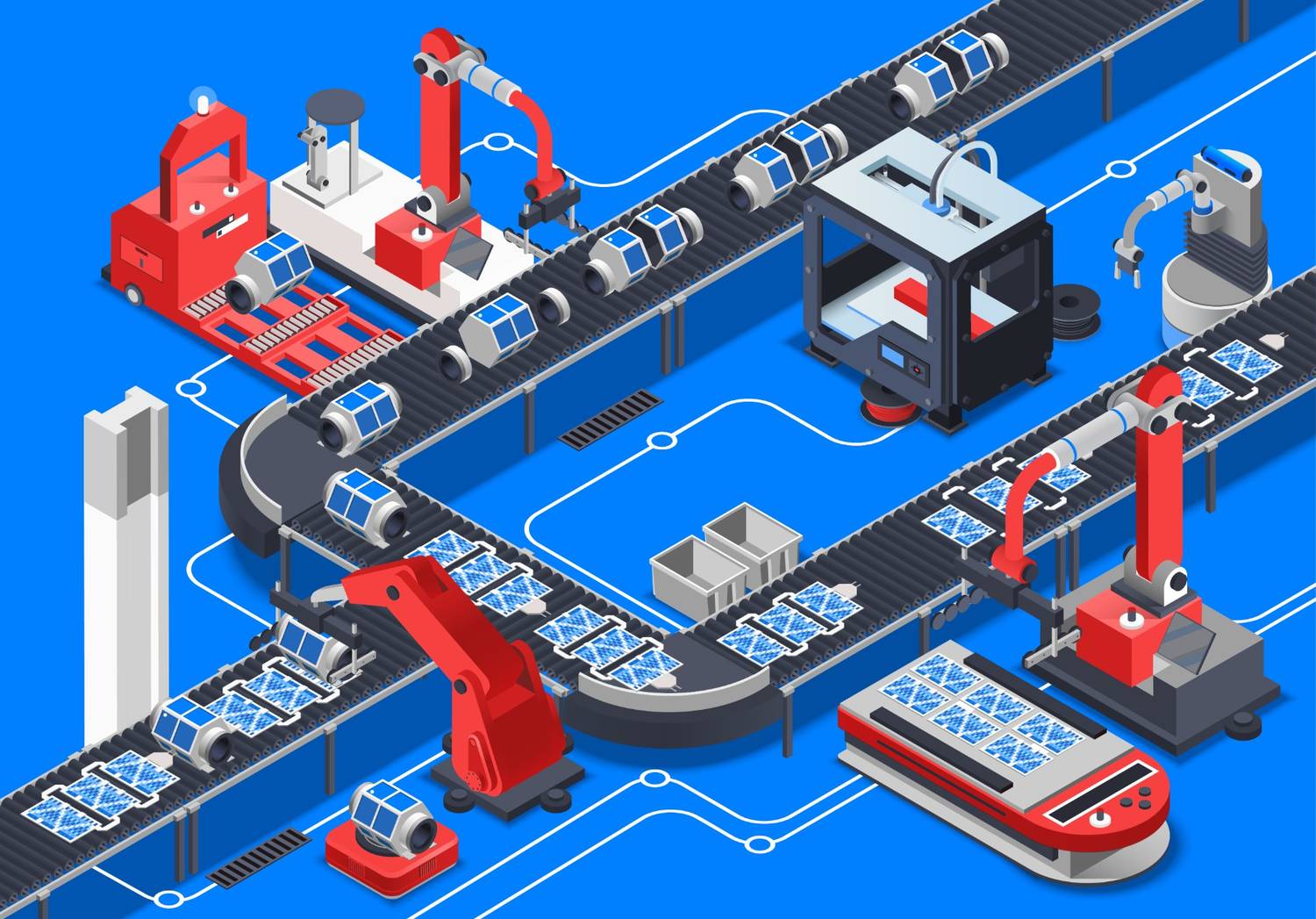
Industry 4.0, or the Fourth Industrial Revolution, represents the current phase of manufacturing, and it is characterized by the integration of smart technologies, data analytics, and connectivity. It builds upon the automation of Industry 3.0, but goes much further by embedding intelligence into machines and operations.
The primary technology driving Industry 4.0 is the Internet of Things (IoT), which allows machines and devices to communicate with each other and exchange data in real time. In manufacturing, this means machines can monitor their own performance, predict maintenance needs, and adjust production schedules without human intervention.
Another key development in Industry 4.0 is advanced robotics. Unlike the fixed robots of Industry 3.0, Industry 4.0 robots are collaborative and can work alongside human operators.
Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (AI) also play a crucial role in Industry 4.0 by enabling manufacturers to analyze vast amounts of data to improve decision-making, predict trends, and optimize production processes.
Industry 4.0 also emphasizes cyber-physical systems, which combine physical components (machines and tools) with software and data analytics.
How Has Manufacturing Changed in India with Industry 4.0?
India has embraced the changes brought by Industry 4.0, with both large enterprises and small-to-medium enterprises (SMEs) adopting automation, robotics, and AI-driven technologies. The Indian government has also launched initiatives such as Make in India to encourage digital transformation and manufacturing excellence.
Many Indian companies are integrating IoT and AI in their factories to optimize operations. For instance, companies in the automotive, textile, and electronics industries are using data analytics to reduce waste, increase energy efficiency, and improve product quality.
India’s smart manufacturing sector is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, with sectors like automobile manufacturing and consumer electronics leading the charge.
Be Part of the Future of Manufacturing with VMS
From the steam engines of Industry 1.0 to the smart factories of Industry 4.0, manufacturing has come a long way. Each industrial revolution has introduced innovations that have significantly improved the efficiency, scalability, and flexibility of production processes.
The future of manufacturing is bright, with Industry 4.0 paving the way for smarter, more connected, and automated production systems. As technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics continue to advance, manufacturing plants will become even more agile, efficient, and sustainable.
For manufacturers looking to optimize their operations in the digital age, VMS Consultants offers expertise in engineering, architecture, and project management services. With our deep understanding of modern industrial needs, we help design and implement state-of-the-art solutions tailored to your manufacturing facility’s requirements.
Contact VMS Consultants today to ensure your manufacturing plant is ready for the future.